In today’s interconnected digital landscape, understanding how content spreads is crucial for anyone seeking to amplify their message. Viral loops are the engines of online dissemination, the mechanisms by which a piece of content, be it a video, article, or social media post, can ignite and spread rapidly across the internet, reaching a massive audience. This article delves into the dynamics of the viral loop, exploring the key components that contribute to its effectiveness and providing insights into how to leverage these principles to create content that resonates and spreads like wildfire.
Viral marketing leverages the power of the viral loop, transforming ordinary users into passionate advocates for a brand or idea. Understanding the underlying principles of viral content is paramount to crafting effective marketing strategies. By examining successful viral campaigns and dissecting the elements that propel them to widespread recognition, we can unlock the secrets to crafting engaging, shareable content that captures the attention of online audiences and generates organic growth through the viral loop.
What is a Viral Loop?
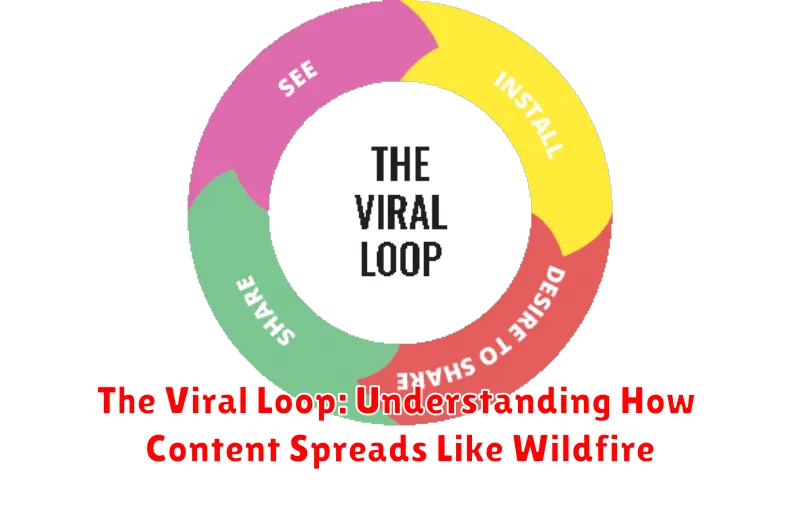
A viral loop is a self-perpetuating cycle where existing users of a product or service encourage new users to join, leading to exponential growth. It’s the mechanism behind content or products spreading rapidly, much like a virus. Each new user has the potential to bring in more users, creating a cascading effect.
The core principle of a viral loop is built-in sharing or referral. This can take many forms, from inviting friends to join a platform to sharing content on social media. The easier and more incentivized the sharing mechanism, the more effective the viral loop becomes.
A successful viral loop is designed to be seamless and integrated into the user experience. It shouldn’t feel forced or intrusive but rather a natural extension of using the product or engaging with the content.
The Key Components of a Viral Loop
A successful viral loop relies on a few key components working together seamlessly. The first is the seed, which is the initial user base or the starting point of the viral spread. This could be your existing customer base, early adopters, or a targeted marketing campaign.
Next, there needs to be a clear action that users take which triggers the viral spread. This could be sharing content, inviting friends, or recommending a product. This action should be simple, intuitive, and highly incentivized.
The propagation mechanism is the channel through which the viral spread occurs. This can vary from social media platforms and email to word-of-mouth and in-app referrals.
Finally, the viral loop needs a strong incentive that motivates users to perform the desired action. This could be a reward, discount, exclusive access, or even the simple satisfaction of helping their friends.
Different Types of Viral Loops
Viral loops can be categorized into several key types, each leveraging different mechanics to drive growth. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for tailoring your strategy effectively.
Network Effects Loops: These loops rely on the inherent value proposition increasing as more users join. Think social media platforms: the more friends you have on the network, the more valuable the platform becomes. This creates an organic incentive for existing users to invite others.
Content Loops: These loops leverage engaging, shareable content to attract new users. A classic example is a viral video that encourages viewers to share it with their networks. The content itself acts as the driver for growth.
Incentivized Loops: These loops offer tangible rewards for sharing or inviting others. Referral programs are a common example, where users receive a discount or other benefit for bringing in new customers. The incentive motivates sharing and drives the loop.
Examples of Successful Viral Loops
Examining successful viral loops provides valuable insights into practical application. Here are a few examples illustrating different approaches:
Dropbox: Referral Program
Dropbox employed a powerful referral program. Existing users received extra storage space for each new user they referred. This incentivized sharing and fueled rapid growth, as both the referrer and the new user benefited.
Hotmail: Email Signature
In its early days, Hotmail included a simple “Get Your Free Email at Hotmail” signature in every outgoing email sent by its users. This passive yet effective approach exposed the service to a broad audience through existing communication channels.
Airbnb: Social Sharing Integration
Airbnb facilitates sharing of listings on social media platforms. This allows users to easily share interesting properties with their networks, generating organic visibility and driving traffic to the platform.
Measuring the Success of Your Viral Loop
Accurately measuring the effectiveness of your viral loop is crucial for optimizing its performance and achieving your desired growth. Key metrics provide insights into the health and efficiency of your loop, allowing for data-driven adjustments and improvements.
A primary metric is the viral coefficient (K-factor). This measures how many new users each existing user brings into the loop. A K-factor greater than 1 signifies exponential growth, while a value less than 1 indicates the loop is not self-sustaining.
Cycle time is another important metric, representing the time it takes for a user to invite another user. A shorter cycle time leads to faster growth. Track this to identify bottlenecks and streamline the invitation process.
Also consider measuring the viral reach, which quantifies the total number of users reached through the viral loop. This metric helps assess the overall impact of your viral strategy.
By carefully monitoring these key metrics, you can gain a clear understanding of your viral loop’s performance and make informed decisions to maximize its impact.
Strategies for Creating Viral Content
Creating content that spreads rapidly requires a strategic approach. Understanding your audience is paramount. Craft content that resonates with their interests, values, and online behaviors. Ask yourself what they would want to share with their networks.
Evoke strong emotions. Content that triggers joy, amusement, surprise, or even controversy has a higher chance of going viral. However, avoid negativity or harmful content, as this can damage your brand.
Keep it simple and shareable. Easy-to-digest content, such as short videos, catchy infographics, and concise text posts, performs well. Ensure the content is easily shareable across various platforms by incorporating social sharing buttons.
Seed your content strategically. Identify and collaborate with key influencers or communities who can help amplify your message. Early adoption by these individuals can significantly boost visibility and reach.
Incorporate a clear call to action. Encourage engagement and sharing by explicitly asking users to like, comment, share, or participate in a challenge related to the content.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing a Viral Loop
Implementing a viral loop successfully requires careful planning and execution. Overlooking key aspects can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Ignoring User Experience: A cumbersome or confusing user experience can quickly deter sharing. Friction in the process, such as requiring too many steps or complex registration forms, can stifle virality.
Overlooking Incentives: While not always necessary, incentives can significantly boost sharing. Ensure any rewards offered are valuable to the target audience and easy to obtain.
Neglecting Mobile Optimization: With a significant portion of internet traffic coming from mobile devices, ensuring your viral loop functions seamlessly across different platforms is crucial.
Forcing Virality: Don’t pressure users to share. Authenticity is key. Focus on creating genuinely valuable content that users will want to share organically.
Failing to Measure Results: Tracking key metrics is essential to understanding what works and what doesn’t. Analyze data to optimize your viral loop for better performance.
The Importance of User Experience in a Viral Loop
A seamless and intuitive user experience is crucial for a successful viral loop. If users encounter friction or confusion during the sharing process, the loop is likely to break down. A positive user experience, however, encourages continued engagement and fuels viral growth.
Simplicity is paramount. The sharing mechanism should be easily understood and executed with minimal steps. Complicated processes or unclear instructions can deter users from participating.
Speed is also a key factor. A slow loading time or a cumbersome sharing process can frustrate users and interrupt the flow of the viral loop. Optimize for speed to ensure a smooth and efficient experience.
Finally, the user experience should be enjoyable. A positive and rewarding experience encourages users not only to complete the loop themselves but also to share it with others. This positive association reinforces the viral spread.